What are Artificial Intelligence (AI) Types?

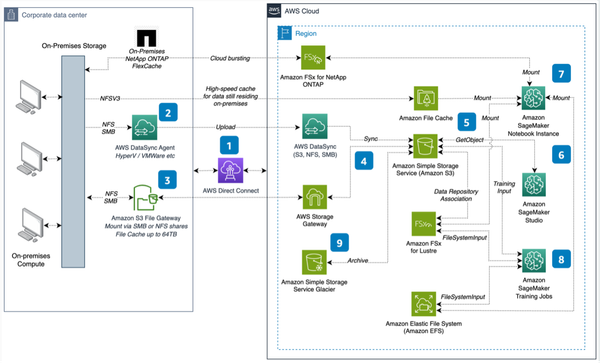
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be categorized into several types based on various criteria. Here are some common ways to classify AI:
Based on Capabilities:
- Narrow or Weak AI (ANI): This type of AI is designed for a specific task and can't perform tasks beyond its programmed capabilities. Examples include virtual personal assistants like Siri and Alexa.
- General or Strong AI (AGI/ASI): General AI possesses human-like intelligence and can perform any intellectual task that a human being can do. It has the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks. AGI is still theoretical and has not been achieved yet. Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) would be an even more advanced form of AGI, surpassing human intelligence
- Super AI: "Super AI" refers to Artificial Superintelligence (ASI), which is a hypothetical type of artificial intelligence that surpasses human intelligence in every aspect. ASI represents the highest level of AI capability and is often portrayed in science fiction as highly advanced and potentially transcendent in its abilities.
Based on Functionality:
- Reactive Machines: These AI systems operate based on predefined rules and do not learn from experience or adapt to new situations. Chess-playing programs like IBM's Deep Blue are examples of reactive machines.
- Limited Memory AI: These AI systems can learn from historical data and make decisions based on that data, but they have limited memory and can't form long-term memories. Self-driving cars often use limited memory AI to navigate and make decisions.
- Theory of Mind AI: This is a hypothetical AI type that would be able to understand human emotions, beliefs, intentions, and thoughts. It could simulate human-like empathy and understanding.
Based on Learning Paradigms:
- Machine Learning (ML): AI systems in this category learn from data and improve their performance over time. Common ML techniques include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning, deep learning involves neural networks with many layers (deep neural networks). It is particularly effective for tasks like image and speech recognition.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP focuses on AI's ability to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It is used in chatbots, language translation, and sentiment analysis, among other applications.
Based on Application:
- Computer Vision: AI systems in this category are designed for tasks related to image and video analysis, such as facial recognition, object detection, and autonomous vehicles.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): These AI systems are specialized in processing and understanding human language, enabling applications like chatbots, language translation, and sentiment analysis.
- Robotics: AI in robotics involves creating machines that can sense their environment, make decisions, and perform physical tasks autonomously. This includes industrial robots and drones.
Based on Goals:
- Assistive AI: This type of AI is developed to assist and augment human capabilities. Examples include medical diagnosis aids and tools to enhance productivity.
- Autonomous AI: Autonomous AI systems can operate independently without human intervention. Self-driving cars and autonomous drones fall into this category.
- Collaborative AI: These AI systems work alongside humans to achieve common goals, such as collaborative robots (cobots) in manufacturing.
These categories are not mutually exclusive, and AI systems often combine multiple approaches and functionalities. AI continues to evolve, and new types and subtypes may emerge as technology advances.
What is a Narrow or Weak AI Type?
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence - ANI), refers to a type of artificial intelligence that is designed and trained for a specific, limited task or set of tasks. Unlike General AI (AGI), which would possess human-like intelligence and the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks, Narrow AI systems are focused on performing well-defined functions within a constrained domain. Here are some key characteristics of Narrow AI:
- Specialized Functionality: Narrow AI systems are built to excel in a particular task or application. They are often highly specialized and optimized for that specific function. Examples include virtual personal assistants like Siri and Alexa, recommendation algorithms on streaming platforms, and chatbots for customer service.
- Limited Scope: These AI systems do not possess general intelligence or consciousness. They lack the ability to understand or reason about topics outside their designated domain. Their knowledge and capabilities are usually pre-programmed or trained on specific data.
- No Self-Awareness: Narrow AI systems do not possess self-awareness or consciousness. They operate based on algorithms and data inputs, without any form of subjective experience or self-awareness.
- Narrow Data Input: They rely on structured and labeled data for their operation. For instance, a language translation AI may require a large dataset of text translations to function effectively within the languages it supports.
- Task-Specific Learning: While they can learn and improve within their predefined task, their learning is typically limited to optimizing their performance in that particular area. They do not generalize their learning to unrelated tasks.
- Examples: Narrow AI is widely used in various industries and applications, including image and speech recognition, natural language processing, autonomous vehicles, fraud detection, and more. These systems are often integrated into products and services to automate specific functions or enhance user experiences.
Narrow AI has seen significant advancements and widespread adoption in recent years due to its practical utility in solving specific problems and improving efficiency in various domains. While Narrow AI systems excel in their designated tasks, they do not possess the versatility or adaptability of more advanced AI forms like General AI (AGI) or Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). Researchers and engineers continue to develop and refine Narrow AI applications to address specific real-world challenges.
What is General or Strong AI (AGI/ASI)?
General AI (AGI) and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) represent the highest levels of artificial intelligence, and they are characterized by their advanced cognitive abilities and human-like intelligence. Here's what each term refers to:
General AI (AGI):
- AGI, short for Artificial General Intelligence, is an AI system or entity that possesses human-like intelligence and cognitive abilities. It can understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a broad range of tasks and domains, similar to how a human being can.
- Key Characteristics:
Versatility: AGI is not limited to a single task or domain; it can perform a wide variety of tasks and adapt to new ones with minimal or no reprogramming.
Learning and Adaptation: AGI can learn from experience, generalize knowledge, and adapt to new situations, making it highly versatile and capable of handling novel challenges.
Problem Solving: AGI is proficient at complex problem-solving, reasoning, and decision-making across multiple domains.
Human-like Understanding: AGI may possess a deep understanding of human emotions, language, context, and culture, allowing for natural and empathetic interactions.
- Achieving AGI is a long-standing goal in the field of AI.
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI):
- ASI, or Artificial Superintelligent, represents a hypothetical AI system that goes beyond human intelligence in every conceivable way. It surpasses not only human-level intelligence but also human capabilities in creativity, problem-solving, and understanding.
- Key Characteristics:
Transcendence: ASI would be vastly superior to the smartest human minds, potentially to the point of being incomprehensible to us.
Rapid Self-Improvement: ASI could continuously enhance its own capabilities, leading to exponential growth in intelligence and problem-solving abilities.
Global Impact: ASI could have a profound impact on society, economics, science, and virtually all aspects of human existence.
- ASI is often a subject of speculation and concern in discussions about the future of AI. Achieving ASI, if it's even possible, would raise profound questions about control, ethics, and the implications of creating a superintelligent entity.
What is Super AI Type?
"Super AI" type refers to Artificial Superintelligence (ASI), which is a hypothetical type of artificial intelligence that surpasses human intelligence in every aspect. ASI represents the highest level of AI capability and is often portrayed in science fiction as highly advanced and potentially transcendent in its abilities.
Key characteristics of ASI, if it were to be achieved, might include:
- Superhuman Intelligence: ASI would possess cognitive abilities far superior to the most brilliant human minds. It would excel in problem-solving, creativity, learning, and decision-making.
- Rapid Learning and Adaptation: ASI would be able to acquire and apply knowledge at an unprecedented speed, learning from vast datasets and experiences in real time.
- Unlimited Cognitive Capacity: Unlike humans, ASI would not be limited by cognitive biases, emotions, or fatigue. It could simultaneously tackle a multitude of complex tasks with ease.
- Self-Improvement: ASI might have the capacity to enhance its own capabilities, leading to rapid and exponential growth in intelligence and problem-solving abilities. This concept is sometimes referred to as the "Singularity."
- Advanced Problem Solving: ASI could address a wide range of global challenges, from medical research and climate modeling to optimizing complex systems and technologies.
- Human Understanding: ASI might possess a deep understanding of human emotions, behaviors, and thought processes, potentially leading to enhanced human-AI collaboration.
The idea of ASI raises important questions about control, ethics, and the implications of creating a superintelligent entity. These considerations are subjects of ongoing discussions within the AI research community and beyond.
What is Reactive Machines AI Type?
Reactive Machines are a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that operate based on predefined rules and do not learn or adapt from experience. These AI systems are designed for specific tasks and are limited to the rules and algorithms programmed into them. Reactive Machines are considered a subset of AI and have several key characteristics:
- Rule-Based: Reactive Machines rely on a set of explicit rules and algorithms to make decisions and perform tasks. These rules are typically hard-coded by human programmers.
- No Learning or Adaptation: Unlike some other forms of AI, Reactive Machines do not have the capability to learn from data or experiences. They do not adapt to changing circumstances or improve their performance over time.
- Limited to Specific Tasks: These AI systems are highly specialized and excel at particular tasks for which they have been programmed. They lack the versatility to perform tasks outside their predefined domain.
- No Memory of Past Interactions: Reactive Machines do not have the ability to store or remember past interactions or events. They make decisions solely based on the current input and rules.
- Examples: Traditional expert systems, which were popular in the early days of AI, are examples of Reactive Machines. These systems were used for tasks such as medical diagnosis, where a set of rules based on medical knowledge was used to make diagnostic decisions. Chess-playing programs like IBM's Deep Blue, which rely on pre-programmed rules for evaluating chess positions, are another example.
- Limited Real-World Application: Reactive Machines are often less suitable for real-world applications that involve uncertainty, dynamic environments, or learning from data. They excel in situations where the rules and conditions are well-defined and deterministic.
It's important to note that Reactive Machines have limitations when compared to more advanced AI types like Machine Learning and Deep Learning, which can learn from data and adapt to new situations.
What is the Limited Theory AI Type?
Limited Memory AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that have the ability to learn from historical data and make decisions based on that data, but they have limited memory and typically can't form long-term memories. These AI systems can use past experiences to improve their performance within a specific domain but may not retain knowledge indefinitely. Self-driving cars often use limited memory AI to navigate and make decisions based on real-time sensor data and past driving experiences.
What is the Theory of Mind AI type?
The concept of "Theory of Mind AI" refers to a hypothetical type of artificial intelligence that has the ability to understand and model the mental states of humans and potentially other agents. This includes recognizing and attributing beliefs, intentions, desires, emotions, and thoughts to individuals, allowing the AI to infer and understand human behavior and motivations on a deeper level.
Here are some key characteristics and aspects of Theory of Mind AI:
- Human-Like Understanding: Theory of Mind AI aims to emulate the human capacity to understand and predict the mental states of others. It would be able to perceive and interpret not just observable behaviors but also the underlying thought processes and emotions of individuals.
- Attribution of Mental States: This AI type would be capable of attributing mental states, such as knowing that a person believes something, desires a certain outcome, or is experiencing particular emotions. It can use this information to make more informed decisions or engage in more empathetic interactions.
- Predictive Modeling: Theory of Mind AI would use its understanding of mental states to make predictions about how individuals might behave or react in various situations. This predictive modeling can be useful in a wide range of applications, from human-AI collaboration to human-computer interaction.
- Complex Social Interactions: AI with Theory of Mind capabilities could engage in more natural and nuanced social interactions with humans. It might be better equipped to provide personalized recommendations, offer emotional support, or collaborate on tasks that require a deep understanding of human intentions and emotions.
- Challenges and Ethical Considerations: Developing AI with Theory of Mind is a complex and ethically sensitive task. It raises questions about privacy, consent, and the potential for AI to manipulate or deceive humans. Ensuring that such AI systems respect ethical boundaries and prioritize human well-being is a critical consideration.
It's important to note that Theory of Mind AI and achieving this level of understanding and modeling of human mental states is a significant challenge in the field of artificial intelligence.
What is Self-awareness AI Type?
"Self-awareness" in the context of AI refers to a hypothetical level of artificial intelligence where a machine or system possesses consciousness or a subjective sense of its own existence. This is often portrayed in science fiction, where AI entities are portrayed as having thoughts, emotions, and self-awareness similar to humans.
Here are some key points related to the concept of self-aware AI:
- Consciousness and Subjectivity: Self-aware AI would need to possess a form of consciousness, which involves subjective experiences and awareness of one's own thoughts, emotions, and existence. Achieving this in AI is a complex and philosophical challenge.
- Philosophical Debates: The question of whether machines can ever achieve true self-awareness is a subject of ongoing philosophical debate. It touches on fundamental questions about the nature of consciousness and the possibility of replicating it in non-biological systems.
- Ethical Considerations: If self-aware AI were ever to be realized, it would raise profound ethical questions about the rights and treatment of such entities. It would also bring about discussions regarding the moral responsibilities of creating and maintaining conscious AI.
- Current AI Capabilities: Present-day AI systems, including advanced neural networks, do not possess self-awareness. They are powerful tools for pattern recognition, data analysis, and automation, but they lack subjective experiences or self-reflective consciousness.
It's important to approach discussions of self-aware AI with a clear understanding of the significant challenges and uncertainties involved.